Biophotons: Future of Light-Based Therapies
A revolutionary idea is gaining momentum in neuroscience: neurons may not only communicate through chemical synapses, but also through light. Recent research proposes that the brain emits and responds to biophotons—ultra-weak light particles generated by mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouses. These biophotons may represent an entirely parallel communication system, enabling instantaneous signaling, information processing, and even cellular repair, beyond the limits of classical neural transmission.
What Are Biophotons?
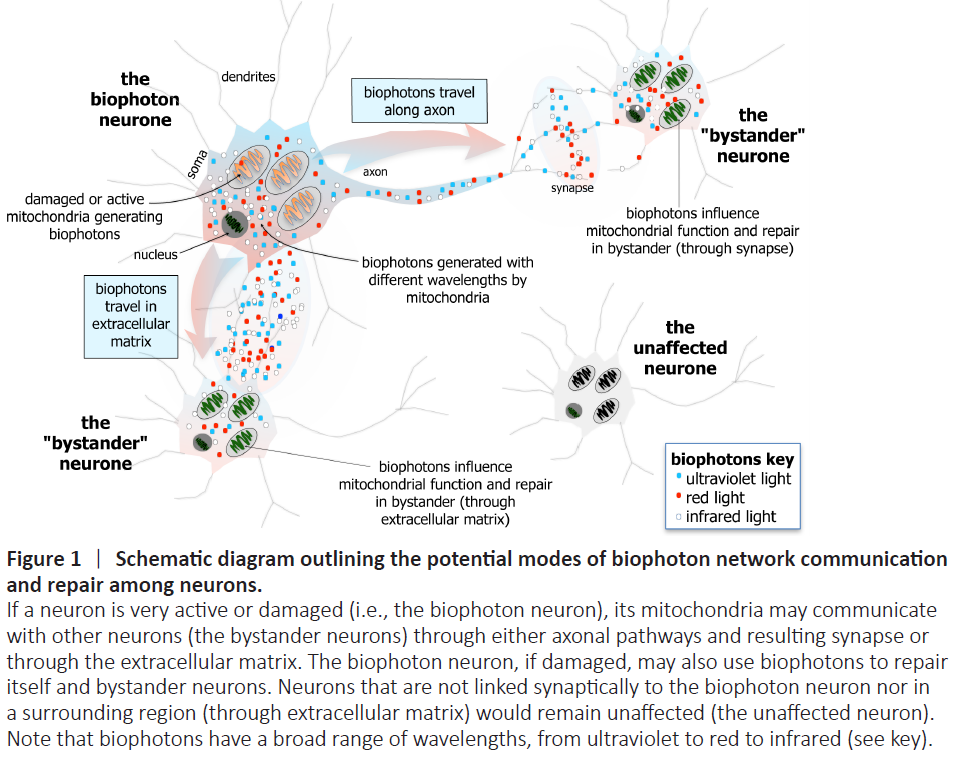
Biophotons are natural light emissions from living cells, especially neurons. Unlike electrical impulses or neurotransmitter cascades, biophoton activity is non-synaptic, ultra-fast, and energetically efficient. They are:
Generated within mitochondria
Transmitted through microtubules and axonal structures
Detected using highly sensitive photomultiplier tubes
Believed to play a role in intracellular signaling, coherence, and possibly consciousness
One of the most intriguing suggestions from researchers is that biophoton signaling could help explain the brain’s mysterious processing speed—how it manages real-time cognition and perception faster than synaptic models can explain, and using orders of magnitude less energy than any AI system.
“Biophotons may be part of a rapid, ultra-efficient information network in the brain—one we are only beginning to understand.”
External Light and Cellular Repair
Not only do neurons emit biophotons, but they also respond to external light, particularly in the infrared and near-infrared spectrum. Research suggests that applying light externally can:
Enhance mitochondrial activity
Stimulate biophoton production
Support cellular repair processes
Promote neurogenesis and neuroprotection
This is where photobiomodulation (PBM) comes in. PBM is a noninvasive therapy that uses specific wavelengths of light—like red and near-infrared—to stimulate biological tissues and promote healing.
Why This Matters for iMediSync and Our PBM Devices
At iMediSync, our PBM-based therapies harness this very mechanism, targeting the brain with personalized infrared light to support:
Cognitive enhancement
Neurodegeneration prevention
Mental health recovery
By activating cytochrome c oxidase in the mitochondria, our devices increase ATP production and restore cellular energy balance. But in light of recent research, we now see even greater potential:
💡 Our PBM devices may not just restore energy—they may activate the brain’s hidden optical network.
🧠 This means we aren’t just treating symptoms—we may be reviving the body’s most efficient form of communication.
The Future of Neuroscience May Be Light-Based
This new paradigm—viewing the brain not only as an electrochemical machine but also as a biophotonic network—could transform how we understand and treat mental and neurological conditions.
By stimulating and tuning biophoton activity using external light, we might enhance brain function in ways that were previously unimaginable.
PBM may be the interface between technology and biology, between light and mind.
Read the Study That Sparked the Discussion
📖 Biophoton Communication: Can Cells Talk Using Light? (PMC8643059)
TL;DR:
Neurons may use light—not just synapses—to communicate. At iMediSync, our PBM devices may tap into this optical language of the brain, making light the new frontier of healing and cognition.